结构体、文字显示与GDT/IDT初始化

代码的优化及结构体使用
昨天的bootpack.c文件中直接把分辨率、内存地址写入了程序中。但这些数据应该从asmhead.nas中获取。harib02a做的就是这类工作,harib02b中引入了C语言中的结构体。
复制代码
把 \30天自制操作系统\projects\05_day\harib02b 复制到 \30天自制操作系统\tolset。
bootpack.c文件
void io_hlt(void);/* 计算机进入待机模式 */
void io_cli(void);/* 禁止中断 */
void io_out8(int port, int data);/* 显示输出 */
int io_load_eflags(void); /* 记录中断许可标志的值 */
void io_store_eflags(int eflags); /* 恢复中断许可标志 */
void init_palette(void);
void set_palette(int start, int end, unsigned char *rgb);
void boxfill8(unsigned char *vram, int xsize, unsigned char c, int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1);
void init_screen(char *vram, int x, int y);
#define COL8_000000 0
#define COL8_FF0000 1
#define COL8_00FF00 2
#define COL8_FFFF00 3
#define COL8_0000FF 4
#define COL8_FF00FF 5
#define COL8_00FFFF 6
#define COL8_FFFFFF 7
#define COL8_C6C6C6 8
#define COL8_840000 9
#define COL8_008400 10
#define COL8_848400 11
#define COL8_000084 12
#define COL8_840084 13
#define COL8_008484 14
#define COL8_848484 15
struct BOOTINFO { /* 声明结构体 */
char cyls, leds, vmode, reserve;
short scrnx, scrny;
char *vram;
};
void HariMain(void)
{
char *vram;
int xsize, ysize;
struct BOOTINFO *binfo;
init_palette();
binfo = (struct BOOTINFO *) 0x0ff0; /* 0x0ff0作为结构体的首地址 */
xsize = (*binfo).scrnx;
ysize = (*binfo).scrny;
vram = (*binfo).vram;
init_screen(vram, xsize, ysize);
for (;;) {
io_hlt();
}
}
void init_palette(void)
{
static unsigned char table_rgb[16 * 3] = {
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, /* 0:黒 */
0xff, 0x00, 0x00, /* 1:亮红 */
0x00, 0xff, 0x00, /* 2:亮绿 */
0xff, 0xff, 0x00, /* 3:亮黄 */
0x00, 0x00, 0xff, /* 4:亮蓝 */
0xff, 0x00, 0xff, /* 5:亮紫 */
0x00, 0xff, 0xff, /* 6:浅暗蓝 */
0xff, 0xff, 0xff, /* 7:白 */
0xc6, 0xc6, 0xc6, /* 8:亮灰 */
0x84, 0x00, 0x00, /* 9:暗红 */
0x00, 0x84, 0x00, /* 10:暗绿 */
0x84, 0x84, 0x00, /* 11:暗黄 */
0x00, 0x00, 0x84, /* 12:暗青 */
0x84, 0x00, 0x84, /* 13:暗紫 */
0x00, 0x84, 0x84, /* 14:浅暗蓝 */
0x84, 0x84, 0x84 /* 15:暗灰 */
};
set_palette(0, 15, table_rgb);
return;
}
void set_palette(int start, int end, unsigned char *rgb)
{
int i, eflags;
eflags = io_load_eflags(); /* 用eflags记录中断许可标志的值 */
io_cli(); /* 中断许可标志的值置0,禁止中断 */
io_out8(0x03c8, start);
for (i = start; i <= end; i++) {
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[0] / 4);
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[1] / 4);
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[2] / 4);
rgb += 3;
}
io_store_eflags(eflags); /* 恢复中断许可标志 */
return;
}
void boxfill8(unsigned char *vram, int xsize, unsigned char c, int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1)
{
int x, y;
for (y = y0; y <= y1; y++) {
for (x = x0; x <= x1; x++)
vram[y * xsize + x] = c;
}
return;
}
void init_screen(char *vram, int x, int y)
{
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_008484, 0, 0, x - 1, y - 29);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_C6C6C6, 0, y - 28, x - 1, y - 28);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 0, y - 27, x - 1, y - 27);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_C6C6C6, 0, y - 26, x - 1, y - 1);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 3, y - 24, 59, y - 24);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 2, y - 24, 2, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, 3, y - 4, 59, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, 59, y - 23, 59, y - 5);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_000000, 2, y - 3, 59, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_000000, 60, y - 24, 60, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, x - 47, y - 24, x - 4, y - 24);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, x - 47, y - 23, x - 47, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, x - 47, y - 3, x - 4, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, x - 3, y - 24, x - 3, y - 3);
return;
}
这段代码乍一看多了很多东西实际上只是用void init_screen(char *vram, int x, int y)函数把boxfill8函数进行统一调用,同时用结构体存储asmhead.nas中的CYLS、LEDS、SCRNX……等数据。结构体在内存中是连续的,但因为内存对齐,中间允许存在空洞。本段代码中不存在。
以下代码要和asmhead.nas中的地址相对应
struct BOOTINFO { /* 声明结构体 */
char cyls, leds, vmode, reserve;
short scrnx, scrny;
char *vram;
};
void HariMain(void)
{ ……
struct BOOTINFO *binfo;
……
binfo = (struct BOOTINFO *) 0x0ff0; /* 0x0ff0作为结构体的首地址 */
……
}
CYLS EQU 0x0ff0 ; 设置引导扇区
LEDS EQU 0x0ff1
VMODE EQU 0x0ff2 ; 颜色位数
SCRNX EQU 0x0ff4 ; x分辨率
SCRNY EQU 0x0ff6 ; y分辨率
VRAM EQU 0x0ff8 ; 图像缓冲区(显存)开始地址
因为0x0ff0被赋值给binfo的首地址,所以asmhead.nas中的常量被bootpack.c文件中的结构体所引用。
bootpack.c文件中结构体和asmhead.nas中常量对应关系
- cyls CYLS 地址:0x0ff0
- leds LEDS 地址:0x0ff1
- vmode VMODE 地址:0x0ff2
- reserve 地址:0x0ff3(asmhead.nas无此定义)
- scrnx SCRNX 地址:0x0ff4
- scrny SCRNY 地址:0x0ff6 (short类型占16位,需要占用2存储单元)
- *vram VRAM 地址:0x0ff8
harib02c中仅仅把指针赋值语(xsize = (*binfo).scrnx;)句改为->(binfo->scrnx),仅仅是书写方式不同。
显示字符
之前的显示字符需要调用bios中断,当前已经进入32位开发模式,无法调用bios中断。所以需要自己手动显示。其实这次还是修改显示的颜色而已。以8×16位2进制序列表示文字,1为显示的像素。
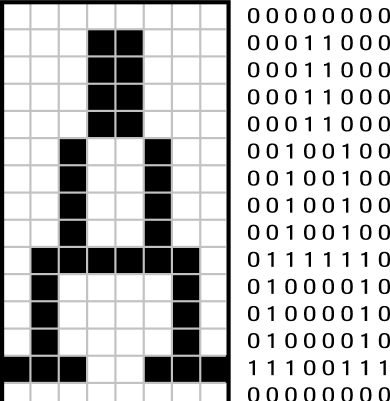
第一行全0的十六进制是0x00,第二行0x18,第三行0x18……以此类推,到左后一行的二进制为0x00。整个字符以行为单位的序列为0x00, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x24, 0x24, 0x24,0x24, 0x7e, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0xe7, 0x00, 0x00。
复制代码
把 \30天自制操作系统\projects\05_day\harib02d 复制到 \30天自制操作系统\tolset。
bootpack.c文件
void io_hlt(void);/* 计算机进入待机模式 */
void io_cli(void);/* 禁止中断 */
void io_out8(int port, int data);/* 显示输出 */
int io_load_eflags(void); /* 记录中断许可标志的值 */
void io_store_eflags(int eflags); /* 恢复中断许可标志 */
void init_palette(void);
void set_palette(int start, int end, unsigned char *rgb);
void boxfill8(unsigned char *vram, int xsize, unsigned char c, int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1);
void init_screen(char *vram, int x, int y);
void putfont8(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, char *font);
#define COL8_000000 0
#define COL8_FF0000 1
#define COL8_00FF00 2
#define COL8_FFFF00 3
#define COL8_0000FF 4
#define COL8_FF00FF 5
#define COL8_00FFFF 6
#define COL8_FFFFFF 7
#define COL8_C6C6C6 8
#define COL8_840000 9
#define COL8_008400 10
#define COL8_848400 11
#define COL8_000084 12
#define COL8_840084 13
#define COL8_008484 14
#define COL8_848484 15
struct BOOTINFO { /* 声明结构体 */
char cyls, leds, vmode, reserve;
short scrnx, scrny;
char *vram;
};
void HariMain(void)
{
struct BOOTINFO *binfo = (struct BOOTINFO *) 0x0ff0;
static char font_A[16] = { /* 声明字符A */
0x00, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x24, 0x24, 0x24,
0x24, 0x7e, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0xe7, 0x00, 0x00
};
init_palette();
init_screen(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, binfo->scrny);
putfont8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 10, 10, COL8_FFFFFF, font_A);
for (;;) {
io_hlt();
}
}
void init_palette(void)
{
static unsigned char table_rgb[16 * 3] = {
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, /* 0:黒 */
0xff, 0x00, 0x00, /* 1:亮红 */
0x00, 0xff, 0x00, /* 2:亮绿 */
0xff, 0xff, 0x00, /* 3:亮黄 */
0x00, 0x00, 0xff, /* 4:亮蓝 */
0xff, 0x00, 0xff, /* 5:亮紫 */
0x00, 0xff, 0xff, /* 6:浅暗蓝 */
0xff, 0xff, 0xff, /* 7:白 */
0xc6, 0xc6, 0xc6, /* 8:亮灰 */
0x84, 0x00, 0x00, /* 9:暗红 */
0x00, 0x84, 0x00, /* 10:暗绿 */
0x84, 0x84, 0x00, /* 11:暗黄 */
0x00, 0x00, 0x84, /* 12:暗青 */
0x84, 0x00, 0x84, /* 13:暗紫 */
0x00, 0x84, 0x84, /* 14:浅暗蓝 */
0x84, 0x84, 0x84 /* 15:暗灰 */
};
set_palette(0, 15, table_rgb);
return;
/* static char 柦椷偼丄僨乕僞偵偟偐巊偊側偄偗偳DB柦椷憡摉 */
}
void set_palette(int start, int end, unsigned char *rgb)
{
int i, eflags;
eflags = io_load_eflags(); /* 用eflags记录中断许可标志的值 */
io_cli(); /* 中断许可标志的值置0,禁止中断 */
io_out8(0x03c8, start);
for (i = start; i <= end; i++) {
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[0] / 4);
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[1] / 4);
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[2] / 4);
rgb += 3;
}
io_store_eflags(eflags); /* 恢复中断许可标志 */
return;
}
void boxfill8(unsigned char *vram, int xsize, unsigned char c, int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1)
{
int x, y;
for (y = y0; y <= y1; y++) {
for (x = x0; x <= x1; x++)
vram[y * xsize + x] = c;
}
return;
}
void init_screen(char *vram, int x, int y)
{
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_008484, 0, 0, x - 1, y - 29);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_C6C6C6, 0, y - 28, x - 1, y - 28);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 0, y - 27, x - 1, y - 27);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_C6C6C6, 0, y - 26, x - 1, y - 1);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 3, y - 24, 59, y - 24);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 2, y - 24, 2, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, 3, y - 4, 59, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, 59, y - 23, 59, y - 5);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_000000, 2, y - 3, 59, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_000000, 60, y - 24, 60, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, x - 47, y - 24, x - 4, y - 24);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, x - 47, y - 23, x - 47, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, x - 47, y - 3, x - 4, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, x - 3, y - 24, x - 3, y - 3);
return;
}
void putfont8(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, char *font)
{
int i;
char *p, d /* data */;
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
p = vram + (y + i) * xsize + x;
d = font[i];
if ((d & 0x80) != 0) { p[0] = c; }
if ((d & 0x40) != 0) { p[1] = c; }
if ((d & 0x20) != 0) { p[2] = c; }
if ((d & 0x10) != 0) { p[3] = c; }
if ((d & 0x08) != 0) { p[4] = c; }
if ((d & 0x04) != 0) { p[5] = c; }
if ((d & 0x02) != 0) { p[6] = c; }
if ((d & 0x01) != 0) { p[7] = c; }
}
return;
}
整个程序新增了以下部分
void HariMain(void)
{
……
static char font_A[16] = { /* 声明字符A */
0x00, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x24, 0x24, 0x24,
0x24, 0x7e, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0xe7, 0x00, 0x00
};
……
putfont8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 10, 10, COL8_FFFFFF, font_A);
}其中static char font_A[16]声明了字符A的二进制表示,putfont8函数是显示字符A在屏幕的左上角。
显示字符函数
void putfont8(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, char *font)
{
int i;
char *p, d /* data */;
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
p = vram + (y + i) * xsize + x;
d = font[i];
if ((d & 0x80) != 0) { p[0] = c; }
if ((d & 0x40) != 0) { p[1] = c; }
if ((d & 0x20) != 0) { p[2] = c; }
if ((d & 0x10) != 0) { p[3] = c; }
if ((d & 0x08) != 0) { p[4] = c; }
if ((d & 0x04) != 0) { p[5] = c; }
if ((d & 0x02) != 0) { p[6] = c; }
if ((d & 0x01) != 0) { p[7] = c; }
}
return;
}函数的参数分别是传入显存地址(char *vram),传入X轴分辨率(int xsize),传入x,y坐标(int x, int y),传入显示字符的颜色(char c),传入显示的字符(char *font)。
函数本身也不算难,参数传入后声明一个指针*p作为显存的起始位置,和数据d用来存font_A中的显示数据,之后用for语句循环16次,依次显示字符A每一行的颜色,每次循环用if语句做差错控制,判断font_A中char元素的每一位是否是0,是0则执行吓一条if语句,不是0要把当前P所指的显存单元中的值换成函数声明中char c的值,也就是所指的颜色。
最后输出,左上角显示了字符A。
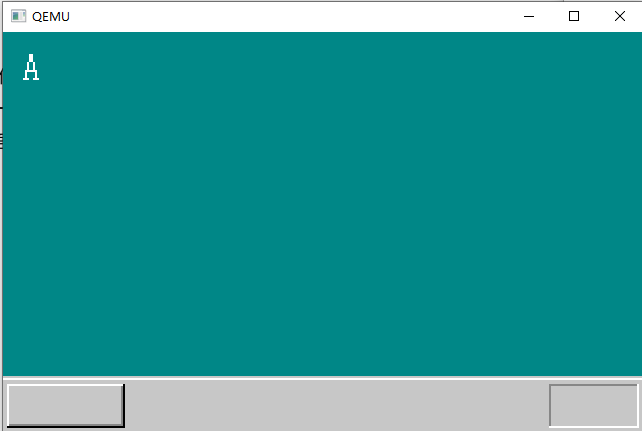
添加字体
作者在这里采用了现成的字体,这个字体以“.”和“*”标志来标识字体。
复制代码
把 \30天自制操作系统\projects\05_day\harib02e 复制到 \30天自制操作系统\tolset。
其中hankaku.txt文件便是字体文件。部分内容如下所示
char 0x50
........
*****...
.*...*..
.*....*.
.*....*.
.*....*.
.*...*..
.****...
.*......
.*......
.*......
.*......
.*......
****....
........
........
char 0x51
........
..***...
.*...*..
*.....*.
*.....*.
*.....*.
*.....*.
*.....*.
*.....*.
*.....*.
*..*..*.
*...*.*.
.*...*..
..***.*.
........
........由于这并非编程语言,所以需要专用的编译器。作者已经提供了。文件中共256个字符。每个字符用8×16位表示。同时这份字体文件也保持了和ASCII码相同的编码顺序,A为0x41。编译好之后想在C语言中调入这份字体,只需要声明以下代码即可。
extern char hankaku[4096];
若想显示特定字符例如A,只需要hankaku + ‘A’ * 16代码即可
harib02e的bootpack.c文件中仅仅多出了以下部分
void HariMain(void)
{
struct BOOTINFO *binfo = (struct BOOTINFO *) 0x0ff0;
extern char hankaku[4096];
init_palette();
init_screen(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, binfo->scrny);
putfont8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 8, 8, COL8_FFFFFF, hankaku + 'A' * 16);
putfont8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 16, 8, COL8_FFFFFF, hankaku + 'B' * 16);
putfont8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 24, 8, COL8_FFFFFF, hankaku + 'C' * 16);
putfont8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 40, 8, COL8_FFFFFF, hankaku + '1' * 16);
putfont8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 48, 8, COL8_FFFFFF, hankaku + '2' * 16);
putfont8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 56, 8, COL8_FFFFFF, hankaku + '3' * 16);
for (;;) {
io_hlt();
}
}同时删除了static char font_A[16]数组
static char font_A[16] = { /* 声明字符A */
0x00, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x18, 0x24, 0x24, 0x24,
0x24, 0x7e, 0x42, 0x42, 0x42, 0xe7, 0x00, 0x00
};运行程序
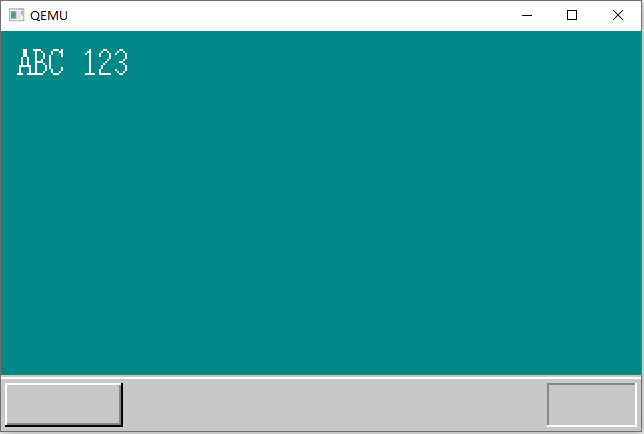
由于void HariMain(void)中使用putfont8函数显示字符,所以每个字符都要调用一次,显得程序很臃肿。harib02f中添加了void putfonts8_asc(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, unsigned char *s)函数,用来显示字符串。
void HariMain(void)
{
struct BOOTINFO *binfo = (struct BOOTINFO *) 0x0ff0;
init_palette();
init_screen(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, binfo->scrny);
putfonts8_asc(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 8, 8, COL8_FFFFFF, "ABC 123");
putfonts8_asc(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 31, 31, COL8_000000, "Haribote OS.");
putfonts8_asc(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 30, 30, COL8_FFFFFF, "Haribote OS.");
for (;;) {
io_hlt();
}
}
void putfonts8_asc(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, unsigned char *s)
{
extern char hankaku[4096];
for (; *s != 0x00; s++) {
putfont8(vram, xsize, x, y, c, hankaku + *s * 16);
x += 8;
}
return;
}C语言中,字符串默认以0x00结尾所以putfonts8_asc函数中循环显示字符串时要判断*s != 0x00。
运行结果
注意:字符串“Haribote OS”添加了阴影效果,这就是为什么Haribote OS被调用了两次。
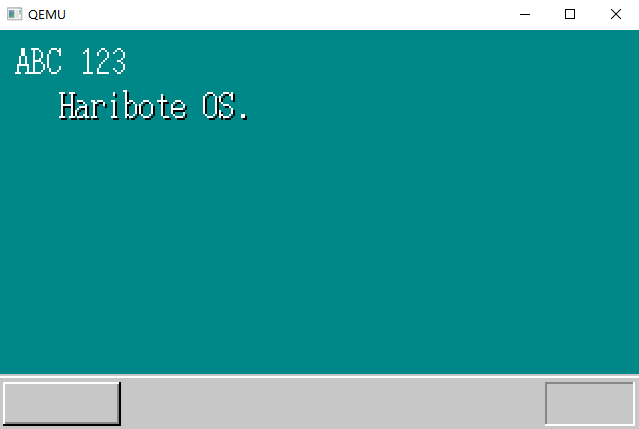
显示变量的值
这里使用sprintf()函数显示内存单元中所存放数据的值
复制代码g
把 \30天自制操作系统\projects\05_day\harib02g 复制到 \30天自制操作系统\tolset
bootpack.c代码也没什么,添加了stdio.h头文件,声明了char s[40];数组,使用了一次sprintf()函数把内存单元的值格式化为字符串,保存在s数组中。之后调用putfonts8_asc函数显示出来。
#include <stdio.h>
void HariMain(void)
{
struct BOOTINFO *binfo = (struct BOOTINFO *) 0x0ff0;
char s[40];
init_palette();
init_screen(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, binfo->scrny);
putfonts8_asc(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 8, 8, COL8_FFFFFF, "ABC 123");
putfonts8_asc(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 31, 31, COL8_000000, "Haribote OS.");
putfonts8_asc(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 30, 30, COL8_FFFFFF, "Haribote OS.");
sprintf(s, "scrnx = %d", binfo->scrnx);
putfonts8_asc(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 16, 64, COL8_FFFFFF, s);
for (;;) {
io_hlt();
}
}运行结果
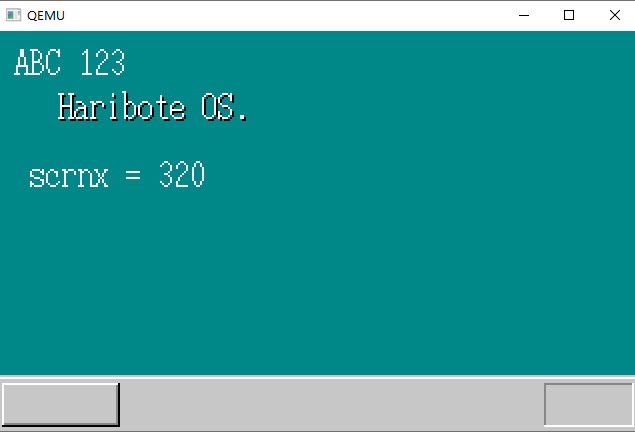
显示鼠标指针
复制代码g
把 \30天自制操作系统\projects\05_day\harib02h 复制到 \30天自制操作系统\tolset
bootpack.c文件,这次改动比较多
#include <stdio.h>
void io_hlt(void);/* 计算机进入待机模式 */
void io_cli(void);/* 禁止中断 */
void io_out8(int port, int data);/* 显示输出 */
int io_load_eflags(void); /* 记录中断许可标志的值 */
void io_store_eflags(int eflags); /* 恢复中断许可标志 */
void init_palette(void);
void set_palette(int start, int end, unsigned char *rgb);
void boxfill8(unsigned char *vram, int xsize, unsigned char c, int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1);
void init_screen8(char *vram, int x, int y);
void putfont8(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, char *font);
void putfonts8_asc(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, unsigned char *s);
void init_mouse_cursor8(char *mouse, char bc);
void putblock8_8(char *vram, int vxsize, int pxsize,
int pysize, int px0, int py0, char *buf, int bxsize);
#define COL8_000000 0
#define COL8_FF0000 1
#define COL8_00FF00 2
#define COL8_FFFF00 3
#define COL8_0000FF 4
#define COL8_FF00FF 5
#define COL8_00FFFF 6
#define COL8_FFFFFF 7
#define COL8_C6C6C6 8
#define COL8_840000 9
#define COL8_008400 10
#define COL8_848400 11
#define COL8_000084 12
#define COL8_840084 13
#define COL8_008484 14
#define COL8_848484 15
struct BOOTINFO {
char cyls, leds, vmode, reserve;
short scrnx, scrny;
char *vram;
};
void HariMain(void)
{
struct BOOTINFO *binfo = (struct BOOTINFO *) 0x0ff0;
char s[40], mcursor[256];
int mx, my;
init_palette();
init_screen8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, binfo->scrny);
mx = (binfo->scrnx - 16) / 2; /*计算画面中央的坐标*/
my = (binfo->scrny - 28 - 16) / 2;
init_mouse_cursor8(mcursor, COL8_008484);
putblock8_8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 16, 16, mx, my, mcursor, 16);
sprintf(s, "(%d, %d)", mx, my);
putfonts8_asc(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 0, 0, COL8_FFFFFF, s);
for (;;) {
io_hlt();
}
}
void init_palette(void)
{
static unsigned char table_rgb[16 * 3] = {
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, /* 0:黒 */
0xff, 0x00, 0x00, /* 1:亮红 */
0x00, 0xff, 0x00, /* 2:亮绿 */
0xff, 0xff, 0x00, /* 3:亮黄 */
0x00, 0x00, 0xff, /* 4:亮蓝 */
0xff, 0x00, 0xff, /* 5:亮紫 */
0x00, 0xff, 0xff, /* 6:浅暗蓝 */
0xff, 0xff, 0xff, /* 7:白 */
0xc6, 0xc6, 0xc6, /* 8:亮灰 */
0x84, 0x00, 0x00, /* 9:暗红 */
0x00, 0x84, 0x00, /* 10:暗绿 */
0x84, 0x84, 0x00, /* 11:暗黄 */
0x00, 0x00, 0x84, /* 12:暗青 */
0x84, 0x00, 0x84, /* 13:暗紫 */
0x00, 0x84, 0x84, /* 14:浅暗蓝 */
0x84, 0x84, 0x84 /* 15:暗灰 */
};
set_palette(0, 15, table_rgb);
return;
}
void set_palette(int start, int end, unsigned char *rgb)
{
int i, eflags;
eflags = io_load_eflags(); /* 用eflags记录中断许可标志的值 */
io_cli(); /* 中断许可标志的值置0,禁止中断 */
io_out8(0x03c8, start);
for (i = start; i <= end; i++) {
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[0] / 4);
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[1] / 4);
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[2] / 4);
rgb += 3;
}
io_store_eflags(eflags); /* 恢复中断许可标志 */
return;
}
void boxfill8(unsigned char *vram, int xsize, unsigned char c, int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1)
{
int x, y;
for (y = y0; y <= y1; y++) {
for (x = x0; x <= x1; x++)
vram[y * xsize + x] = c;
}
return;
}
void init_screen8(char *vram, int x, int y)
{
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_008484, 0, 0, x - 1, y - 29);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_C6C6C6, 0, y - 28, x - 1, y - 28);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 0, y - 27, x - 1, y - 27);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_C6C6C6, 0, y - 26, x - 1, y - 1);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 3, y - 24, 59, y - 24);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 2, y - 24, 2, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, 3, y - 4, 59, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, 59, y - 23, 59, y - 5);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_000000, 2, y - 3, 59, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_000000, 60, y - 24, 60, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, x - 47, y - 24, x - 4, y - 24);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, x - 47, y - 23, x - 47, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, x - 47, y - 3, x - 4, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, x - 3, y - 24, x - 3, y - 3);
return;
}
void putfont8(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, char *font)
{
int i;
char *p, d /* data */;
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
p = vram + (y + i) * xsize + x;
d = font[i];
if ((d & 0x80) != 0) { p[0] = c; }
if ((d & 0x40) != 0) { p[1] = c; }
if ((d & 0x20) != 0) { p[2] = c; }
if ((d & 0x10) != 0) { p[3] = c; }
if ((d & 0x08) != 0) { p[4] = c; }
if ((d & 0x04) != 0) { p[5] = c; }
if ((d & 0x02) != 0) { p[6] = c; }
if ((d & 0x01) != 0) { p[7] = c; }
}
return;
}
void putfonts8_asc(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, unsigned char *s)
{
extern char hankaku[4096];
for (; *s != 0x00; s++) {
putfont8(vram, xsize, x, y, c, hankaku + *s * 16);
x += 8;
}
return;
}
void init_mouse_cursor8(char *mouse, char bc)
/* 准备鼠标指针(16 x 16) */
{
static char cursor[16][16] = {
"**************..",
"*OOOOOOOOOOO*...",
"*OOOOOOOOOO*....",
"*OOOOOOOOO*.....",
"*OOOOOOOO*......",
"*OOOOOOO*.......",
"*OOOOOOO*.......",
"*OOOOOOOO*......",
"*OOOO**OOO*.....",
"*OOO*..*OOO*....",
"*OO*....*OOO*...",
"*O*......*OOO*..",
"**........*OOO*.",
"*..........*OOO*",
"............*OO*",
".............***"
};
int x, y;
for (y = 0; y < 16; y++) {
for (x = 0; x < 16; x++) {
if (cursor[y][x] == '*') {
mouse[y * 16 + x] = COL8_000000;
}
if (cursor[y][x] == 'O') {
mouse[y * 16 + x] = COL8_FFFFFF;
}
if (cursor[y][x] == '.') {
mouse[y * 16 + x] = bc;
}
}
}
return;
}
void putblock8_8(char *vram, int vxsize, int pxsize,
int pysize, int px0, int py0, char *buf, int bxsize)
{
int x, y;
for (y = 0; y < pysize; y++) {
for (x = 0; x < pxsize; x++) {
vram[(py0 + y) * vxsize + (px0 + x)] = buf[y * bxsize + x];
}
}
return;
}
为了初始话鼠标显示,定义了函数void init_mouse_cursor8。函数中用static char cursor[16][16]定义了鼠标指针的样式,之后用双重For循环依次读取每个元素并转换为对应的颜色,“*”转化为黑色“O”转化为白色“.”转化为设定好的背景颜色(bc)。之后把转换好的颜色数据存入*mouse指针中。
void init_mouse_cursor8(char *mouse, char bc)
/* 准备鼠标指针(16 x 16) */
{
static char cursor[16][16] = {
"**************..",
"*OOOOOOOOOOO*...",
"*OOOOOOOOOO*....",
"*OOOOOOOOO*.....",
"*OOOOOOOO*......",
"*OOOOOOO*.......",
"*OOOOOOO*.......",
"*OOOOOOOO*......",
"*OOOO**OOO*.....",
"*OOO*..*OOO*....",
"*OO*....*OOO*...",
"*O*......*OOO*..",
"**........*OOO*.",
"*..........*OOO*",
"............*OO*",
".............***"
};
int x, y;
for (y = 0; y < 16; y++) {
for (x = 0; x < 16; x++) {
if (cursor[y][x] == '*') {
mouse[y * 16 + x] = COL8_000000;
}
if (cursor[y][x] == 'O') {
mouse[y * 16 + x] = COL8_FFFFFF;
}
if (cursor[y][x] == '.') {
mouse[y * 16 + x] = bc;
}
}
}
return;
}为了显示鼠标定义了void putblock8_8(char *vram, int vxsize, int pxsize,int pysize, int px0, int py0, char *buf, int bxsize)函数
void putblock8_8(char *vram, int vxsize, int pxsize,
int pysize, int px0, int py0, char *buf, int bxsize)
{
int x, y;
for (y = 0; y < pysize; y++) {
for (x = 0; x < pxsize; x++) {
vram[(py0 + y) * vxsize + (px0 + x)] = buf[y * bxsize + x];
}
}
return;
}其中char *vram, int vxsize和putfonts8_asc中的一样,此处不在介绍。int pxsize,int pysize指的是鼠标的像素尺寸,此处均为16。int px0, int py0是鼠标显示的坐标,可随意指定,但不得越界。char *buf指的是鼠标像素存放的地址。int bxsize指的是鼠标每行的像素数。
函数中,两个for循环分别控制显存中的行和列。之后把mcursor中对应的颜色信息复制到显存中
vram[(py0 + y) * vxsize + (px0 + x)] = buf[y * bxsize + x];
最后运行程序,鼠标出现了
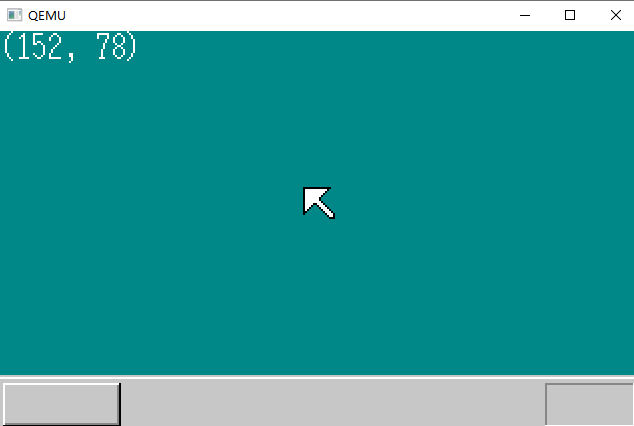
实际上这不是鼠标,只是在屏幕中画出了一个鼠标的图片。
GDT 与 IDT 的初始化
为了制作真正的鼠标,这一节引入段和中断。
所谓段,在现代操作系统中属于内存管理的范畴。程序装入内存中需要指名程序的装载地址,如今的计算机内存相当庞大,即使是消费级PC也能达到TB级别。即便如此也不能将所有程序和数据全部存入内存中。通常计算机内存往往比硬盘空间小很多。为了提高内存利用率引入了分页存储、分段存储这类概念。
说白了就是把内存划分为几个区间,每个区间内的地址从0开始,然后还要个段表/页表来记录每个段/页的地址。而所谓GDT是“global(segment)descriptor table”的缩写,即全局段号记录表。
其中包含了以下信息:
- 段大小
- 段的起始地址
- 段的管理属性(禁止写入,禁止执行,系统专用等)
CPU用8个字节(64位)数据来表示这些信息。但由于段寄存器只有16位且只有高13位可以用,故段号只能表示8192个。所以整个GDT的大小是8192×8=64KB,需要存储在内存中。
IDT是“interrupt descriptor table”的缩写,也就是中断记录表
之前使用的中断都是BIOS所提供。鼠标,键盘等外设与CPU交互都是使用中断方式。如今需要自己提供中断。
把 \30天自制操作系统\projects\05_day\harib02i 复制到 \30天自制操作系统\tolset。
bootpack.c文件
#include <stdio.h>
void io_hlt(void);/* 计算机进入待机模式 */
void io_cli(void);/* 禁止中断 */
void io_out8(int port, int data);/* 显示输出 */
int io_load_eflags(void); /* 记录中断许可标志的值 */
void io_store_eflags(int eflags); /* 恢复中断许可标志 */
void init_palette(void);
void set_palette(int start, int end, unsigned char *rgb);
void boxfill8(unsigned char *vram, int xsize, unsigned char c, int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1);
void init_screen8(char *vram, int x, int y);
void putfont8(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, char *font);
void putfonts8_asc(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, unsigned char *s);
void init_mouse_cursor8(char *mouse, char bc);
void putblock8_8(char *vram, int vxsize, int pxsize,
int pysize, int px0, int py0, char *buf, int bxsize);
#define COL8_000000 0
#define COL8_FF0000 1
#define COL8_00FF00 2
#define COL8_FFFF00 3
#define COL8_0000FF 4
#define COL8_FF00FF 5
#define COL8_00FFFF 6
#define COL8_FFFFFF 7
#define COL8_C6C6C6 8
#define COL8_840000 9
#define COL8_008400 10
#define COL8_848400 11
#define COL8_000084 12
#define COL8_840084 13
#define COL8_008484 14
#define COL8_848484 15
struct BOOTINFO {
char cyls, leds, vmode, reserve;
short scrnx, scrny;
char *vram;
};
struct SEGMENT_DESCRIPTOR {
short limit_low, base_low;
char base_mid, access_right;
char limit_high, base_high;
};
struct GATE_DESCRIPTOR {
short offset_low, selector;
char dw_count, access_right;
short offset_high;
};
void init_gdtidt(void);
void set_segmdesc(struct SEGMENT_DESCRIPTOR *sd, unsigned int limit, int base, int ar);
void set_gatedesc(struct GATE_DESCRIPTOR *gd, int offset, int selector, int ar);
void load_gdtr(int limit, int addr);
void load_idtr(int limit, int addr);
void HariMain(void)
{
struct BOOTINFO *binfo = (struct BOOTINFO *) 0x0ff0;
char s[40], mcursor[256];
int mx, my;
init_palette();
init_screen8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, binfo->scrny);
mx = (binfo->scrnx - 16) / 2; /*计算画面中央的坐标*/
my = (binfo->scrny - 28 - 16) / 2;
init_mouse_cursor8(mcursor, COL8_008484);
putblock8_8(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 16, 16, mx, my, mcursor, 16);
sprintf(s, "(%d, %d)", mx, my);
putfonts8_asc(binfo->vram, binfo->scrnx, 0, 0, COL8_FFFFFF, s);
for (;;) {
io_hlt();
}
}
void init_palette(void)
{
static unsigned char table_rgb[16 * 3] = {
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, /* 0:黒 */
0xff, 0x00, 0x00, /* 1:亮红 */
0x00, 0xff, 0x00, /* 2:亮绿 */
0xff, 0xff, 0x00, /* 3:亮黄 */
0x00, 0x00, 0xff, /* 4:亮蓝 */
0xff, 0x00, 0xff, /* 5:亮紫 */
0x00, 0xff, 0xff, /* 6:浅暗蓝 */
0xff, 0xff, 0xff, /* 7:白 */
0xc6, 0xc6, 0xc6, /* 8:亮灰 */
0x84, 0x00, 0x00, /* 9:暗红 */
0x00, 0x84, 0x00, /* 10:暗绿 */
0x84, 0x84, 0x00, /* 11:暗黄 */
0x00, 0x00, 0x84, /* 12:暗青 */
0x84, 0x00, 0x84, /* 13:暗紫 */
0x00, 0x84, 0x84, /* 14:浅暗蓝 */
0x84, 0x84, 0x84 /* 15:暗灰 */
};
set_palette(0, 15, table_rgb);
return;
}
void set_palette(int start, int end, unsigned char *rgb)
{
int i, eflags;
eflags = io_load_eflags(); /* 用eflags记录中断许可标志的值 */
io_cli(); /* 中断许可标志的值置0,禁止中断 */
io_out8(0x03c8, start);
for (i = start; i <= end; i++) {
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[0] / 4);
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[1] / 4);
io_out8(0x03c9, rgb[2] / 4);
rgb += 3;
}
io_store_eflags(eflags); /* 恢复中断许可标志 */
return;
}
void boxfill8(unsigned char *vram, int xsize, unsigned char c, int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1)
{
int x, y;
for (y = y0; y <= y1; y++) {
for (x = x0; x <= x1; x++)
vram[y * xsize + x] = c;
}
return;
}
void init_screen8(char *vram, int x, int y)
{
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_008484, 0, 0, x - 1, y - 29);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_C6C6C6, 0, y - 28, x - 1, y - 28);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 0, y - 27, x - 1, y - 27);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_C6C6C6, 0, y - 26, x - 1, y - 1);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 3, y - 24, 59, y - 24);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, 2, y - 24, 2, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, 3, y - 4, 59, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, 59, y - 23, 59, y - 5);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_000000, 2, y - 3, 59, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_000000, 60, y - 24, 60, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, x - 47, y - 24, x - 4, y - 24);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_848484, x - 47, y - 23, x - 47, y - 4);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, x - 47, y - 3, x - 4, y - 3);
boxfill8(vram, x, COL8_FFFFFF, x - 3, y - 24, x - 3, y - 3);
return;
}
void putfont8(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, char *font)
{
int i;
char *p, d /* data */;
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
p = vram + (y + i) * xsize + x;
d = font[i];
if ((d & 0x80) != 0) { p[0] = c; }
if ((d & 0x40) != 0) { p[1] = c; }
if ((d & 0x20) != 0) { p[2] = c; }
if ((d & 0x10) != 0) { p[3] = c; }
if ((d & 0x08) != 0) { p[4] = c; }
if ((d & 0x04) != 0) { p[5] = c; }
if ((d & 0x02) != 0) { p[6] = c; }
if ((d & 0x01) != 0) { p[7] = c; }
}
return;
}
void putfonts8_asc(char *vram, int xsize, int x, int y, char c, unsigned char *s)
{
extern char hankaku[4096];
for (; *s != 0x00; s++) {
putfont8(vram, xsize, x, y, c, hankaku + *s * 16);
x += 8;
}
return;
}
void init_mouse_cursor8(char *mouse, char bc)
/* 准备鼠标指针(16 x 16) */
{
static char cursor[16][16] = {
"**************..",
"*OOOOOOOOOOO*...",
"*OOOOOOOOOO*....",
"*OOOOOOOOO*.....",
"*OOOOOOOO*......",
"*OOOOOOO*.......",
"*OOOOOOO*.......",
"*OOOOOOOO*......",
"*OOOO**OOO*.....",
"*OOO*..*OOO*....",
"*OO*....*OOO*...",
"*O*......*OOO*..",
"**........*OOO*.",
"*..........*OOO*",
"............*OO*",
".............***"
};
int x, y;
for (y = 0; y < 16; y++) {
for (x = 0; x < 16; x++) {
if (cursor[y][x] == '*') {
mouse[y * 16 + x] = COL8_000000;
}
if (cursor[y][x] == 'O') {
mouse[y * 16 + x] = COL8_FFFFFF;
}
if (cursor[y][x] == '.') {
mouse[y * 16 + x] = bc;
}
}
}
return;
}
void putblock8_8(char *vram, int vxsize, int pxsize,
int pysize, int px0, int py0, char *buf, int bxsize)
{
int x, y;
for (y = 0; y < pysize; y++) {
for (x = 0; x < pxsize; x++) {
vram[(py0 + y) * vxsize + (px0 + x)] = buf[y * bxsize + x];
}
}
return;
}
void init_gdtidt(void)
{
struct SEGMENT_DESCRIPTOR *gdt = (struct SEGMENT_DESCRIPTOR *) 0x00270000;
struct GATE_DESCRIPTOR *idt = (struct GATE_DESCRIPTOR *) 0x0026f800;
int i;
/* GDT初始化 */
for (i = 0; i < 8192; i++) {
set_segmdesc(gdt + i, 0, 0, 0);
}
set_segmdesc(gdt + 1, 0xffffffff, 0x00000000, 0x4092);
set_segmdesc(gdt + 2, 0x0007ffff, 0x00280000, 0x409a);
load_gdtr(0xffff, 0x00270000);
/* IDT初始化 */
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
set_gatedesc(idt + i, 0, 0, 0);
}
load_idtr(0x7ff, 0x0026f800);
return;
}
void set_segmdesc(struct SEGMENT_DESCRIPTOR *sd, unsigned int limit, int base, int ar)
{
if (limit > 0xfffff) {
ar |= 0x8000; /* G_bit = 1 */
limit /= 0x1000;
}
sd->limit_low = limit & 0xffff;
sd->base_low = base & 0xffff;
sd->base_mid = (base >> 16) & 0xff;
sd->access_right = ar & 0xff;
sd->limit_high = ((limit >> 16) & 0x0f) | ((ar >> 8) & 0xf0);
sd->base_high = (base >> 24) & 0xff;
return;
}
void set_gatedesc(struct GATE_DESCRIPTOR *gd, int offset, int selector, int ar)
{
gd->offset_low = offset & 0xffff;
gd->selector = selector;
gd->dw_count = (ar >> 8) & 0xff;
gd->access_right = ar & 0xff;
gd->offset_high = (offset >> 16) & 0xffff;
return;
}
同时在naskfunc.nas中多了两个函数
_load_gdtr: ; void load_gdtr(int limit, int addr);
MOV AX,[ESP+4] ; limit
MOV [ESP+6],AX
LGDT [ESP+6]
RET
_load_idtr: ; void load_idtr(int limit, int addr);
MOV AX,[ESP+4] ; limit
MOV [ESP+6],AX
LIDT [ESP+6]
RET本次bootpack.c文件中新增的部分
struct SEGMENT_DESCRIPTOR {
short limit_low, base_low;
char base_mid, access_right;
char limit_high, base_high;
};
struct GATE_DESCRIPTOR {
short offset_low, selector;
char dw_count, access_right;
short offset_high;
};
void init_gdtidt(void)
{
struct SEGMENT_DESCRIPTOR *gdt = (struct SEGMENT_DESCRIPTOR *) 0x00270000;
struct GATE_DESCRIPTOR *idt = (struct GATE_DESCRIPTOR *) 0x0026f800;
int i;
/* GDT初始化 */
for (i = 0; i < 8192; i++) {
set_segmdesc(gdt + i, 0, 0, 0);
}
set_segmdesc(gdt + 1, 0xffffffff, 0x00000000, 0x4092);
set_segmdesc(gdt + 2, 0x0007ffff, 0x00280000, 0x409a);
load_gdtr(0xffff, 0x00270000);
/* IDT初始化 */
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
set_gatedesc(idt + i, 0, 0, 0);
}
load_idtr(0x7ff, 0x0026f800);
return;
}
void set_segmdesc(struct SEGMENT_DESCRIPTOR *sd, unsigned int limit, int base, int ar)
{
if (limit > 0xfffff) {
ar |= 0x8000; /* G_bit = 1 */
limit /= 0x1000;
}
sd->limit_low = limit & 0xffff;
sd->base_low = base & 0xffff;
sd->base_mid = (base >> 16) & 0xff;
sd->access_right = ar & 0xff;
sd->limit_high = ((limit >> 16) & 0x0f) | ((ar >> 8) & 0xf0);
sd->base_high = (base >> 24) & 0xff;
return;
}
void set_gatedesc(struct GATE_DESCRIPTOR *gd, int offset, int selector, int ar)
{
gd->offset_low = offset & 0xffff;
gd->selector = selector;
gd->dw_count = (ar >> 8) & 0xff;
gd->access_right = ar & 0xff;
gd->offset_high = (offset >> 16) & 0xffff;
return;
}首先定义了两个结构体
- SEGMENT_DESCRIPTOR
- GATE_DESCRIPTOR
(待续)